Neuro Athletics is a 3x weekly newsletter that breaks down the medical and scientific practises that you need to perform at your peak. Subscribers include professional athletes, athletic trainers, coaches and casual fans. So if you are not already a subscriber, sign up and join 55,000+ others who receive it directly in their inbox each week — it’s free.
Neuro Athletes,
Good skin is not just about appearance; it is also a predictor of brain health. Exercise, including weight training, releases brain protection proteins, enhances cognitive functions, and reshuffles epigenetic tags involved in aging.
The connection between skin and brain health is more profound than often realized, and weight training can be a pivotal factor in maintaining both.
The skin, our body's largest organ, not only acts as a protective barrier but is also part of the neuroendocrine system. As we age, our skin becomes thinner, and signs of aging such as wrinkles and dehydration become evident.
Weight training, however, may offer a remedy for aging skin.
Skin aging is often linked to the degradation of the extracellular matrix (ECM) in the dermis. This degradation leads to a decrease in dermal thickness, resulting in the appearance of aging signs. Various factors contribute to this, including age-related hormonal changes, exposure to sun and pollution, and increased levels of inflammatory cytokines.
Weights vs Wrinkles: The New Approach to Skin Health
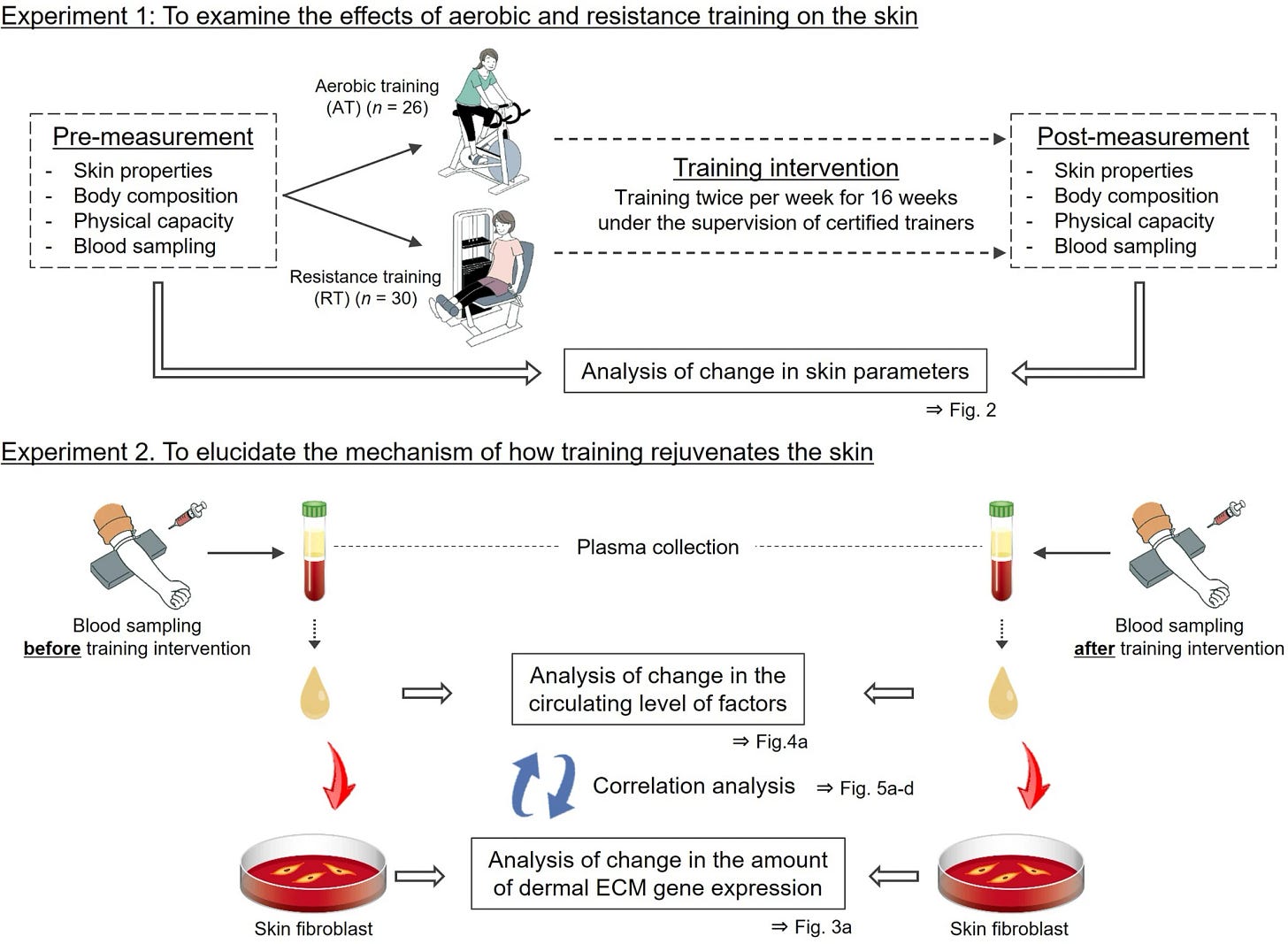
The aging process takes its toll on the skin, resulting in signs like wrinkles, spots, and dehydration. A recent 16-week randomized trial involving 61 sedentary middle-aged Japanese women has unveiled a new approach to counteract these signs of aging. Both aerobic training (AT) and resistance training (RT) were investigated, with intriguing findings.
Aerobic Training (AT)
Effects on the Skin:
Interleukin 15 (IL-15): Aerobic exercise led to increased circulating levels of IL-15, a crucial cytokine that stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis in the skin. Mitochondria are the powerhouse of the cells and their increased biogenesis helps maintain a healthy dermal structure.
Skin Elasticity and Upper Dermal Structure: The participants involved in aerobic training witnessed an improvement in skin elasticity and the upper dermal structure. However, it's noteworthy that this training method didn't lead to improvements in dermal thickness.
Underlying Mechanisms: Aerobic training has a profound impact on the cardiovascular system, leading to improved blood circulation. Enhanced blood flow to the skin might contribute to these observed improvements, providing nourishment to skin cells.
Resistance Training (RT)
Effects on the Skin:
Improving Dermal Thickness: Unlike aerobic training, resistance training specifically counteracted skin aging by improving dermal thickness. This is a critical aspect of youthful skin, as thicker dermis provides better support and less sagging.
Decreasing Circulating Factors: The reduction in circulating levels of specific factors like CCL28, N,N-dimethylglycine, and CXCL4 was observed in resistance training. These factors have been associated with skin aging, and their decrease can slow down the process.
Increasing Dermal BGN Expression: An increase in dermal BGN expression was seen, which codes for biglycan. Biglycan is a vital protein in the skin's extracellular matrix, playing an essential role in maintaining dermal thickness and integrity.
Underlying Mechanisms: Resistance training might exert its effects by creating a hormone-balancing effect and releasing muscle-derived myokines, which can have various positive effects on skin health.
Hyaluronic acid is a crucial element to consider in the quest for youthful skin. Known for its hydrating properties, hyaluronic acid plays an essential role in maintaining skin moisture, thereby aiding in the prevention of wrinkles and dehydration. When combined with weight training, it could enhance skin's elasticity and overall health.
Both aerobic and resistance training appear to have unique and complementary benefits in maintaining and improving skin health. While aerobic training improves elasticity and upper dermal structure, resistance training specifically targets dermal thickness, a key factor in youthful appearance.
These findings suggest that a balanced routine involving both aerobic and resistance training could provide an effective, non-invasive way to rejuvenate the skin. The revelation that exercise is not just good for overall health but can also be a targeted approach to achieve younger skin is transforming our understanding of skin health maintenance.
This groundbreaking study adds to the growing body of evidence that physical activity is a multifaceted tool in health and wellness, including the pursuit of youthful, resilient skin.
What do you think?
Until next time,
Louisa x